 The thought of getting breast cancer strikes fear in most women. Mammograms and breast self-exams (BSEs) are usually recommended to reduce the chances of getting breast cancer. At one point, it was recommended that women 40 and older get a mammogram every other year, then every year starting at age 50. However, the current consensus among most professionals is to recommend various time frames depending on factors such as breast size, medical history, and whether or not
... Read more
The thought of getting breast cancer strikes fear in most women. Mammograms and breast self-exams (BSEs) are usually recommended to reduce the chances of getting breast cancer. At one point, it was recommended that women 40 and older get a mammogram every other year, then every year starting at age 50. However, the current consensus among most professionals is to recommend various time frames depending on factors such as breast size, medical history, and whether or not
... Read more
Portals
Are Mammograms Always Safe?
…
 The thought of getting breast cancer strikes fear in most women. Mammograms and breast self-exams (BSEs) are usually recommended to reduce the chances of getting breast cancer. At one point, it was recommended that women 40 and older get a mammogram every other year, then every year starting at age 50. However, the current consensus among most professionals is to recommend various time frames depending on factors such as breast size, medical history, and whether or not
... Read more
The thought of getting breast cancer strikes fear in most women. Mammograms and breast self-exams (BSEs) are usually recommended to reduce the chances of getting breast cancer. At one point, it was recommended that women 40 and older get a mammogram every other year, then every year starting at age 50. However, the current consensus among most professionals is to recommend various time frames depending on factors such as breast size, medical history, and whether or not
... Read more
Radiological & Non Radiological Testing in Herpes …
 If you have had a cold sore, then you are familiar with the Herpes Simplex Virus. There are two types of the virus, HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 is the virus that produces cold sores on the lips, but it can also cause sores around the genitals.
HSV-2,
... Read more
If you have had a cold sore, then you are familiar with the Herpes Simplex Virus. There are two types of the virus, HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 is the virus that produces cold sores on the lips, but it can also cause sores around the genitals.
HSV-2,
... Read more
Combining Multi-modality Sparse Representation-based …
 Neuroscientists Xu L, Wu X, et al. at the College of Information Science and Technology, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China provide evidence that discrimination between patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment
... Read more
Neuroscientists Xu L, Wu X, et al. at the College of Information Science and Technology, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China provide evidence that discrimination between patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment
... Read more
MRI Assessment May Help to Define Pancreatic …
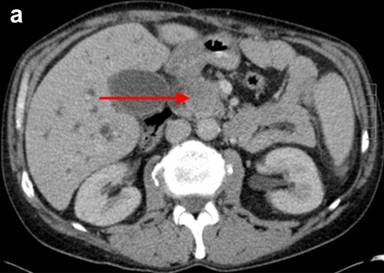 A recent pilot study suggests that MRI assessment may be useful in defining pancreatic inflammation that is associated with type 1 diabetes. The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and authored by
... Read more
A recent pilot study suggests that MRI assessment may be useful in defining pancreatic inflammation that is associated with type 1 diabetes. The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and authored by
... Read more
FDA Approves Pacemaker with MRI Scanning Abilities…
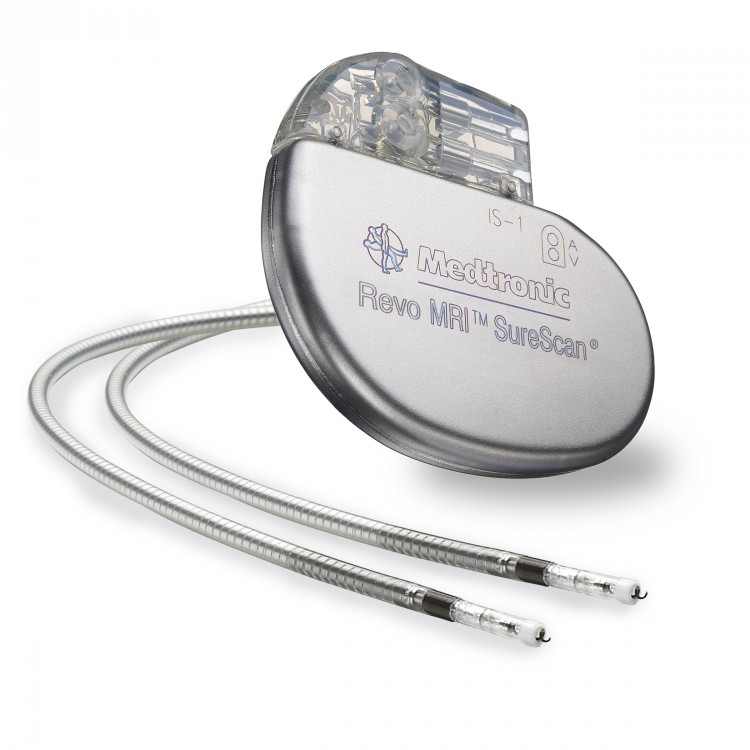 A pacemaker system enables patients to receive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans with a limited exclusion zone.
Biotronik (Berlin, Germany), a manufacturer of cardiovascular medical devices, reported that the US Food and Drug Administration
... Read more
A pacemaker system enables patients to receive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans with a limited exclusion zone.
Biotronik (Berlin, Germany), a manufacturer of cardiovascular medical devices, reported that the US Food and Drug Administration
... Read more
Weak Chemical Forces Combined to Fortify Novel Imaging …
 Associate Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Hyunjoon Kong, graduate student and member of the Regenerative Biology and Tissue Engineering research theme at the Institute for Genomic Biology, Cartney Smith, and colleagues made it a
... Read more
Associate Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Hyunjoon Kong, graduate student and member of the Regenerative Biology and Tissue Engineering research theme at the Institute for Genomic Biology, Cartney Smith, and colleagues made it a
... Read more
Recovery Time Following Concussions Could be Longer …
 A study released on concussion patients employing diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) discovered that males took longer to recover following a concussion than females did. Results of the study, which demonstrate that DTI can be used as a bias-free way to
... Read more
A study released on concussion patients employing diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) discovered that males took longer to recover following a concussion than females did. Results of the study, which demonstrate that DTI can be used as a bias-free way to
... Read more
Targeted Biopsy Neutralizes Low-risk Prostate Cancer…
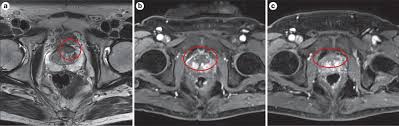 More men who are under the impression that they have low-risk prostate cancers are opting for active surveillance, abandoning treatment and observing the cancer closely with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests, digital rectal exams, and
... Read more
More men who are under the impression that they have low-risk prostate cancers are opting for active surveillance, abandoning treatment and observing the cancer closely with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests, digital rectal exams, and
... Read more
Radiotherapy May Be Improved with New Agent…
 Researchers from The University of Manchester, a branch of the Manchester Cancer Research Centre, have verified the potential of a drug that enhances the overall effectiveness of radiotherapy in halting tumor growth and progression.
Utilizing the
... Read more
Researchers from The University of Manchester, a branch of the Manchester Cancer Research Centre, have verified the potential of a drug that enhances the overall effectiveness of radiotherapy in halting tumor growth and progression.
Utilizing the
... Read more
Page 1 of 379








 pending.FLV.jpg)
